Google Chrome M121 Unveils Game-Changing AI Features for a More Personalized Browsing Experience
Welcome to the next level of browsing! Google Chrome M121 is here with a dazzling array of generative AI features designed to revolutionize your web experience. In this blog post, we’ll explore three groundbreaking features that promise to simplify, enhance, and personalize your browsing journey. Get ready for a Chrome makeover like never before!
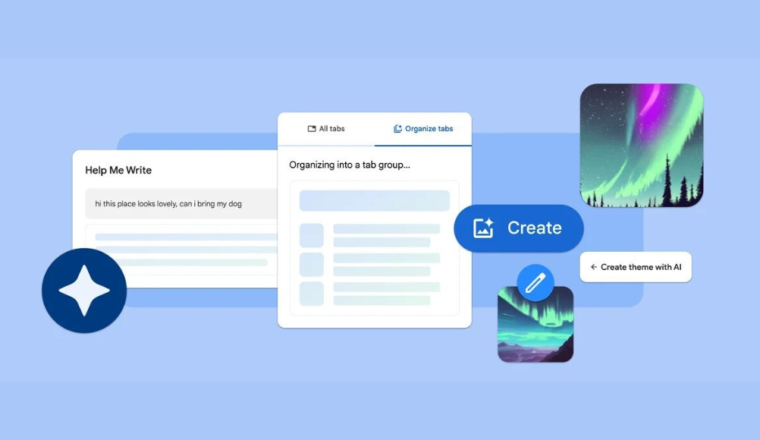
Tab Organizer: Declutter Your Digital Space
Tired of drowning in a sea of open tabs? Chrome’s new Tab Organizer feature is your savior. This innovative tool uses advanced machine learning to automatically group and label similar tabs, putting an end to the chaos. Simply right-click on a tab and choose “Organize Similar Tabs” or click the drop-down arrow to the left of the tabs. Chrome even suggests names and emojis for your tab groups, making navigation a breeze.
Create with AI: Your Theme, Your Way
Inject a personalized touch into your Chrome experience with the Create with AI feature. This tool lets you generate custom themes based on your preferred subject, mood, visual style, and color. Want an “aurora borealis” theme in an “animated” style with a “serene” mood? Just click the “Customize Chrome” button, select “Change theme,” and choose “Create with AI.” Watch as Chrome brings your vision to life using a text-to-image diffusion model, previously seen in Android 14 and Pixel devices.
Help Me Write: AI-Powered Text Assistance
Struggling to find the right words? Say hello to Help Me Write, Chrome’s AI-powered text assistance feature. This tool suggests ways to polish, expand, or adjust the tone of your text based on your preferences. Right-click on any text box or field on a website and choose “Help me write” to unleash the power of generative AI in your writing endeavors. Note: This feature is set to arrive in the next month’s Chrome release.

Google Chrome’s AI Ambitions and Challenges:
As the world’s most popular web browser, Chrome continues to push the boundaries of AI integration. These new features represent Google’s ongoing commitment to innovation. With a global market share of 62.85%, Chrome has already introduced AI features such as real-time video captions, malicious site detection, permission prompt management, and key point generation for web pages.
However, these exciting additions have sparked mixed reviews. While users and experts applaud the convenience and creativity of these AI tools, concerns about privacy, security, and accuracy have been raised. During our exploration of the update, we observed occasional hiccups with the Tab Organizer feature, which sometimes grouped unrelated tabs or failed to function.
Google reassures users that privacy and security are top priorities. The company emphasizes that it neither collects nor stores personal information from these AI features. Constant improvements in AI model quality and reliability are underway, with Google actively seeking user feedback to refine these experimental features.