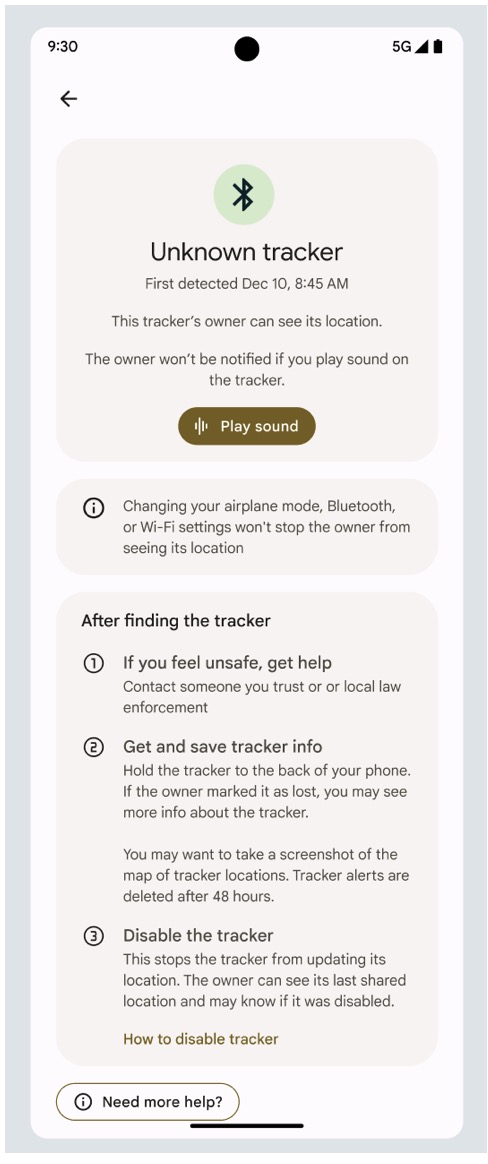
Google Delays Gemini AI Launch
Google has chosen to delay the launch of its highly anticipated Gemini AI model, intended to compete with OpenAI’s GPT-4, until the following year. According to sources cited by The Information, Google CEO Sundar Pichai made the decision to postpone the scheduled launch events in California, New York, and Washington due to performance issues in languages other than English.
Gemini, designed as a multimodal AI model capable of comprehending and generating text, images, and various data types, has encountered challenges in multilingual functionality. In comparison to GPT-4, Gemini falls short in this aspect, prompting Google engineers to recognize the need for further improvement. While smaller versions of Gemini are undergoing testing, the development of the full-scale Gemini model is still in progress.
This isn’t the first instance of a delay for Gemini; earlier reports indicated a pushback for the cloud version of the model. Consequently, AI-driven products like the Bard chatbot, expected to benefit from Gemini enhancements, will now face a delay until the following year.
Google initially unveiled Gemini at its I/O event, emphasizing its impressive multimodal capabilities and efficiency in tool and API integrations. The company planned to offer Gemini in various sizes, including a mobile-friendly “Gecko” version, with the goal of attracting third-party developers.
The key question remains when Gemini will be seamlessly integrated into Google’s services, such as Bard, Search, and Workspace.
Gemini’s Role in Shaping the Future of Internet Information Flow
The significance of Gemini for Google lies in its potential to demonstrate the company’s ability to rival or surpass OpenAI, shaping a new internet landscape where information flow transitions from traditional search and the World Wide Web to chatbots.
Gemini’s success would also challenge the industry perception that GPT-4 is the ultimate benchmark, showcasing that there is still room for breakthroughs in underlying Transformer technology and scaling principles. While Google holds an advantage in data and computing, its ability to capitalize on this advantage has been hindered, in part, by Microsoft’s partnership with OpenAI.
Since March 2023, no company, whether a major tech player or an innovative startup, whether operating with closed or open source models, has managed to release a model comparable to GPT-4. Instead, the market is flooded with language models at the GPT-3.5 level, a standard that now seems easily attainable.
GPT-4’s advanced capabilities stem from its larger, more complex, and more expensive architecture. Using a mixture of interconnected AI models (a Mixture of Experts), GPT-4 surpasses a single large model. It is speculated that Google’s Gemini is built on a similar concept. OpenAI’s CEO, Sam Altman, has hinted at a timeline for the release of GPT-5, expected to be even more advanced.
However, the intricate architecture of these models also comes with a high cost for inference. In response, OpenAI is striving to lower prices with models like GPT-4 Turbo, even if it means compromising on some aspects of quality.